The Ultimate Guide To Coplanting
The Ultimate Guide to Companion Planting
Companion planting is a gardening practice that involves planting certain types of plants together to benefit each other. This can be done to attract beneficial insects, deter pests, improve soil quality, or increase yields.
There are many different ways to companion plant, and the specific combinations that work best will vary depending on the plants you are growing and your climate. However, there are some general principles that can help you get started.
Benefits of Companion Planting
There are many benefits to companion planting, including:
- Increased yields: Companion planting can help to increase yields by attracting beneficial insects, deterring pests, and improving soil quality.
- Improved soil quality: Companion plants can help to improve soil quality by fixing nitrogen, suppressing weeds, and attracting earthworms.
- Disease resistance: Companion plants can help to increase disease resistance by attracting beneficial insects that prey on pests.
- Flavor enhancement: Some companion plants can enhance the flavor of other plants.
- Visual appeal: Companion planting can also add visual appeal to your garden by creating interesting and attractive combinations of plants.
Types of Companion Planting
There are two main types of companion planting:
- Attracting Beneficial Insects: Some plants attract beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps. These insects help to control pests by eating them. For example, marigolds attract ladybugs, which help to control aphids.
- Deterring Pests: Some plants deter pests by emitting chemicals that repel them. For example, mint deters mosquitoes, and garlic deters cabbage moths.
- Improving Soil Quality: Some plants fix nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth. For example, beans fix nitrogen, so they are often planted with corn, which is a heavy feeder.
- Increasing Yields: Some plants can increase the yields of other plants by providing shade, support, or other benefits. For example, tomatoes benefit from being planted with basil, which helps to deter pests and improve the flavor of the tomatoes.
How to Companion Plant
There are a few things to keep in mind when companion planting:
- Consider the needs of your plants: When choosing companion plants, it is important to consider the needs of your plants. For example, if you are growing tomatoes, you will need to choose companion plants that do not require a lot of water.
- Pay attention to the height and spread of your plants: When choosing companion plants, it is also important to pay attention to the height and spread of your plants. You don't want to plant two plants that will compete for space.
- Experiment: The best way to learn about companion planting is to experiment. Try different combinations of plants and see what works best for you.
Here are some specific companion planting combinations that you can try:
- Beans and corn: Beans fix nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for corn. Corn provides support for beans, and both plants benefit from each other's shade.
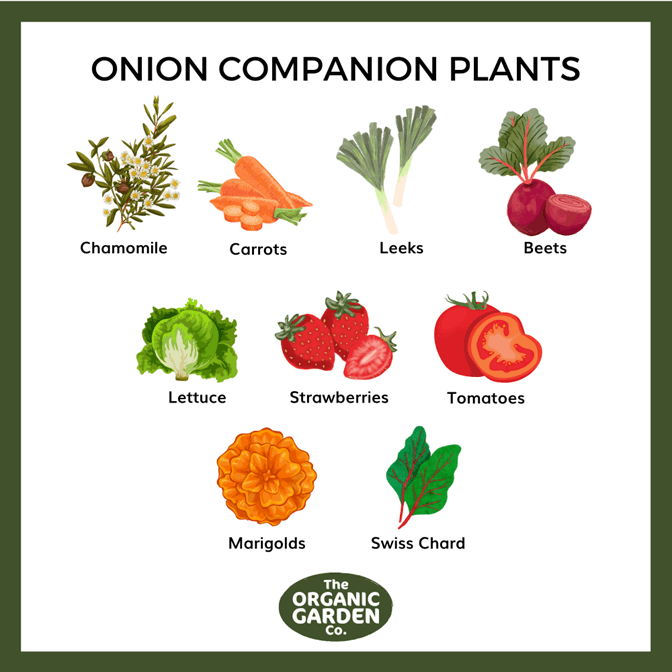
- Carrots and onions: Carrots and onions repel each other's pests. Carrots also help to prevent root knot nematodes, which can damage onions.
- Marigolds and tomatoes: Marigolds attract ladybugs, which help to control aphids, a common pest of tomatoes.
- Basil and tomatoes: Basil helps to deter pests and improve the flavor of tomatoes.
- Peppermint and cabbage: Peppermint deters cabbage moths, a common pest of cabbage.
Conclusion
Companion planting is a great way to improve the health and productivity of your garden. By following the tips in this guide, you can create a thriving garden that is full of delicious, healthy food.
Co planting, also known as companion planting, is a gardening technique where two or more plants are grown together for mutual benefit. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as planting different types of vegetables together, or planting flowers and vegetables together.
There are many benefits to co planting. For example, some plants can help to repel pests, while others can help to improve the soil quality. Co planting can also help to attract pollinators, which can help to increase the yield of your garden.
If you are interested in learning more about co planting, I recommend visiting Gardenia Inspiration. This website has a wealth of information on the topic, including a list of beneficial companion plants, as well as tips for creating a successful co planting garden.
FAQ of co planting
1. What is co-planting?
Co-planting is a gardening technique that involves planting two or more different types of plants together. This can be done in the same bed, pot, or container. There are many benefits to co-planting, including:
- Increased yields: Some plants can benefit each other by attracting pollinators, deterring pests, or providing shade.
- Improved soil health: Different plants can help to improve the soil by adding nutrients, breaking down organic matter, or attracting beneficial insects.
- Reduced pest and disease problems: Some plants can help to repel pests or diseases that would otherwise attack other plants.
- Increased visual appeal: Co-planting can add interest and diversity to your garden.
2. How do I choose which plants to co-plant?
There are a few things to consider when choosing plants to co-plant. First, you need to make sure that the plants have similar growing requirements. They should also have similar light, water, and fertilizer needs.
Second, you need to consider the size of the plants. Some plants, such as tomatoes, will grow very large. You need to make sure that you have enough space for them to grow without crowding out their neighbors.
Third, you need to consider the purpose of your co-planting. Are you trying to increase yields, improve soil health, or deter pests? Once you know your goals, you can choose plants that will help you achieve them.
3. What are some good combinations for co-planting?
Here are some good combinations for co-planting:
- Beans and corn: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits the corn. Corn provides shade for the beans, which helps to keep them cool.
- Carrots and tomatoes: Carrots help to deter the tomato hornworm, a common pest of tomatoes. Tomatoes provide shade for the carrots, which helps to keep them cool.
- Lettuce and spinach: Lettuce and spinach grow well together and have similar growing requirements.
- Marigolds and tomatoes: Marigolds help to repel nematodes, a common pest of tomatoes.
- Peas and radishes: Peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits the radishes. Radishes mature quickly, so you can plant them between the peas and harvest them before the peas start to shade them out.
4. What are some tips for co-planting?
Here are some tips for co-planting:
- Do your research. Before you start co-planting, it's a good idea to do some research to find out which plants are compatible. There are many resources available online and in gardening books.
- Start small. If you're new to co-planting, it's a good idea to start small. Plant a few different combinations in different parts of your garden to see what works best.
- Be flexible. Sometimes, co-planting doesn't work out as planned. If you see that two plants aren't getting along, don't be afraid to replant them.
- Have fun! Co-planting can be a lot of fun. Experiment with different combinations and see what you can create.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when co-planting?
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when co-planting:
- Planting incompatible plants together. Not all plants are compatible with each other. Do your research before you start planting.
- Planting too many plants together. If you plant too many plants together, they may crowd each other out.
- Not considering the size of the plants. Some plants, such as tomatoes, will grow very large. You need to make sure that you have enough space for them to grow without crowding out their neighbors.
- Not watering properly. Co-planted plants may need more or less water than they would if they were planted alone. Monitor your plants closely and adjust your watering schedule as needed.
Image of co planting
5 different images of "co planting" from Pinterest:
- Comfrey and carrots. Comfrey is a nitrogen-fixing plant that can help to improve the soil for carrots. The two plants also benefit each other, as comfrey's large leaves help to shade the carrots, keeping them cool and preventing them from bolting.

- Marigolds and tomatoes. Marigolds are a natural pest repellent, so they can help to protect tomatoes from aphids, whiteflies, and other pests. Marigolds also help to improve the soil's drainage, which is beneficial for tomatoes.

- Basil and tomatoes. Basil and tomatoes are a classic combination, as they complement each other's flavors. Basil also helps to deter tomato pests, such as aphids and whiteflies.

- Lettuce and carrots. Lettuce and carrots can be planted together because they have different water needs. Lettuce needs more water than carrots, so it will help to keep the soil moist for the carrots.
- Peas and beans. Peas and beans are both nitrogen-fixing plants, so they can help to improve the soil for each other. They also benefit each other by providing shade and support.

Post a Comment for "The Ultimate Guide To Coplanting"